More Limbic Cat Brain
Fish evolved in the sea 500million years ago
Mammal-like reptiles evolved 300million years ago
250 million years ago was the Permian extinction in which
most species died
200 million years ago came the first mammals
120 million years ago the early mammals quit laying eggs
Reptiles ruled the earth during the day. They evolved into massive dinosaurs, while
the first mammals of 200 million years ago were tiny nocturnal warm blooded
creatures, which lived underground. In order to survive, early mammals learned to live in groups. Brains that were good at living with others
were more likely to reproduce. Unlike
reptiles, which evolved gained superiority as they became physically larger, mammals
thrived by increasing their biomass through accumulation of allies that could cooperate. Mammals have hair, are warm-blooded, have
middle ear bones, a limbic system and raise their young. Our ability to learn has roots in our
relationships. We have feelings.
The limbic system contains the brain structures of emotional
intelligence and every mammal has one. Also
called the rhinencephalon, or nose brain, it regulates our bodies function through the autonomic
nervous system and hypothalamus and makes up 40% of the rodent brain. Smell directs rodent emotion. Our olfactory portion is only 5% of our
brain. A main difference between the human and
chimpanzee brain is we have 1000 fewer olfactory genes. The neurons in your pituitary and
hypothalamus evolved from cells designed to help our ancestors sense a
potential mate thus the purpose of the limbic system is to influence the
hypothalamus in the spread of our genes.
To the egg a chicken is just a device to create another egg. We also spread our genes when our close relatives procreate since we share genes.
Mammals evolved after reptiles but before primates. Our limbic system mediates social emotions
such as separation, distress, social bonding, playfulness, and maternal
nurturance. A mammal can react
positively to another mammal.
Neurochemicals include neurotransmitters, which stay in the brain and hormones,
which are released into the bloodstream.
These work together in our pursuit of happiness and status. The brain releases happy chemicals in
response to improved survival prospects.
As soon as a mammal meets is immediate survival needs it puts is efforts
into raising its status. Survival and
status are the same since status improves the chance of having surviving
descendants. There is a pecking order among beasts with tails and it has been
found that animals and humans lower in the pecking order have higher cortisol
levels. This negatively impacts both their
prefrontal cortex, which controls executive functioning and immune system
impacting general health. From the stress of poverty glucocorticoids are known to atrophy the
frontal cortex and lower is level of activity. Sapolsky notes that “when humans invented
poverty they came up with a way of subjugating the low ranking like nothing
seen in the primate world.”
The prefrontal cortex is the cortical area intertwined with
the limbic system. Its size in a species
correlates with how large the average social group of the species is. When
there is a choice between something harder that is better in the long run and something
easier it gets you to do the harder thing.
It promotes impulse control, planning and is the last part of the brain to
mature. It is not fully myelinated in
humans until age 25 and it provides emotional regulation for long term planning,
gratification, impulse control, and postponement. It evolved for gossip, social relations and
emotional intelligence. It is what makes us human. The role of the prefrontal cortex was learned
about by what happened to Phineas Gage.
The Marshmallow test if given to 5 year olds can predict
their SAT scores.
You offer Marshmallow now or if they can wait they can have two and the kids
who have a more developed prefrontal cortex choose to wait. There is also a Hide and seek test. If you play hide and seek with 5 year old
they often cant resist telling you where they are and when they count they go
on past ten
Humans create hierarchies just like other primates. When you improve your status in the hierarchy
the brain releases a short burst of the same happy chemicals that it rewards
reproductive success. Dopamine gives the
frontal cortex the energy to push you to do the right thing. When you loose
status the brain releases unhappy chemicals.
Humans usually belong to several ranking systems at the same time and
rank economically, intellectually, socially etc.
We are wired for hierarchy.
When women are at college their periods synchronize to the period of the
socially dominant female that is the most attractive or social.
There are 3 areas of the brain that tend to wear out with
age. When he Substantia nigra goes it
causes a tremor and Parkinson’s. With
damage to the hippocampus memory is impaired, and as frontal cortex looses
neurons we see diminished tests of cognitive function and disinhibited 80 year
olds. People know what they should do
but can’t choose the correct thing. One
looses the ability to plan for the future due to the brain damage of age. This may be why people become conservative as
they age. People who are disciplined have
higher metabolic rates in their prefrontal cortex. People who had lower
prefrontal activity can be sociopaths.
Pre Frontal cortex inhibits the amygdala and The amygdala
tries to inhibit the frontal cortex.
When you are under stress the amygdala silences the frontal cortex and
you get unregulated behavior. Without a
pre frontal cortex the amygdala doesn’t adjust to new situations. If the
harder thing is the scarier thing the frontal cortex can in that situation stimulate
the amygdala.
When you walk in a
room the first thing you do is scan the room to see if there is anything that
can eat you. If there is, the eye sends
a message to the amygdala, which tells the hypothalamus to release stress
hormones (cortisol) and the sympathetic nervous system to release adrenalin. If there are no threats we look to see is
there anything we can eat. Digestion
involves the parasympathetic nervous system. Then we see is there anything we can mate with
and anything that will mate with us. In
rodents this occurs through the nose.
Smell governs rodent emotions. Incidentally for us 90% of taste is
smell. The olfactory neurons are one
synapse away from the limbic system in both rodents and us and thus our noses
motivate us. Thus the limbic system
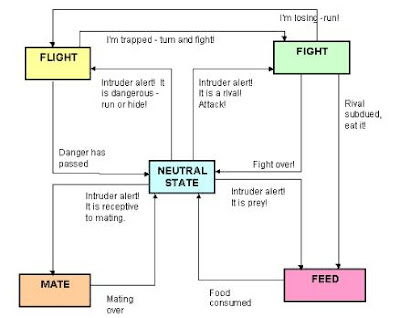
drive the 4 Fs .
There are 7 separate emotion systems in the brain
seeking - anticipation
rage - frustration
fear - pain threat
panic - loss
play - carefree
mating - copulation
who and when
care - maternal
nurturance
each of these has its own specific area in the brain
The limbic system is also involved with memory and includes
the hippocampus. We remember things
best, which are emotionally charged, and this was important for survival. When the brain detects an emotionally charged
event the amygdala releases dopamine, which tells the hippocampus to file
this. We remember how to escape from the
tiger
Relatedness biases us toward cooperation. Pseudo-relatedness (the formation of
artificial groups) can also do this. We
tend to organize in groups. Sapolsky
tells how in the filming of the movie Planet of the Apes the actors playing the
Apes all ate together separately from the actors playing humans. Playing repeated rounds also promotes
cooperation and we are given the opportunity to reciprocate. It has been learned that we have in the
amygdala mirror neurons, which get excited if we and someone else are moving in
synchrony. Another part of the limbic
system the anterior-cingulate has to do with empathy and moral affective decision-making. Since people related to us carry our genes
helping relatives is a way of spreading genes,
An early experience for children is learning when to be
aggressive. How does morality develop in kids. At first kids can distinguish between
inanimate and animate within the first few weeks of life . Normal kids respond to faces while Autistic
kids don’t do this. Kids differentiate
themselves from the world around them. First
they view themselves as continuous with their environment, which is mom. Kid
says I have an owie if mom has a cut.
Then they become aware of others and develop a theory of mind. This starts
at ages 3 – 5 and is this a prerequisite
for empathy. Sociopaths have theory of
mind but they don’t have empathy. Through theory of mind we can gain social
awareness by seeing the world through the motivations of others
Preconventional - you
may get caught or a reward
Conventional - your
motivation based on shared group values
rules laws postconvention moral reasoning – there are things that are
more important bad laws need to be
broken this is the right thing to do
Not every gets to the postconventional stage
Moral development questions include:
How do kids learn that it is ok to lie?
What are Rules and principles?
How do kids learn there are bad laws?
What are Intended harm and successful harm?
What are the effects of growing up in a violent setting? Greater child abuse and greater antisocial behavior
Parents are good for determining what peer groups kids have
access to. Kids learn more from their peers. Emigrant kids pick up the accents of peers over their parents.
If you break kids into groups they have disparaging beliefs
about other groups.
Implicit knowledge is located in the cerebellum.
Studies show moral actions are implicit. If you have to think about whether to cheat,
then you will cheat some of the time.
The people who don’t cheat do it implicitly

No comments:
Post a Comment